Acceleration
Acceleration occurs when there is a change in speed – speeding up or slowing down. It is commonly termed acceleration when the speed is increased and deceleration when the speed is decreased. Acceleration can also be described as a change in direction. You may have seen graphs or diagrams illustrating acceleration – velocity-time graphs and ticker-timers:
Acceleration is a vector so is often described as being positive in one direction and negative in the other. Acceleration is defined as a change in velocity divided by the time interval. The equation for acceleration is:
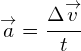
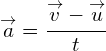
where:
![]() = the acceleration in m/s2
= the acceleration in m/s2
![]() = the final velocity in m/s
= the final velocity in m/s
![]() = the initial velocity in m/s
= the initial velocity in m/s
![]() = the time in s
= the time in s
The equation can be rearranged to calculate any of the variables required.
Example 1:
What is the acceleration of a vehicle that has an initial speed of 3 m/s and it increases its speed to 11 m/s over a time interval of 4 seconds?
using:
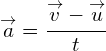
![]()
![]() = 2 m/s2
= 2 m/s2
Example 2:
How long does it take a cyclist to accelerate from rest to 4.5 m/s if they are accelerating at 0.5 m/s?
using:
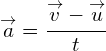
![]()
![]()
![]() = 9 s
= 9 s
